
Unstoppable DeFi is a protocol on Arbitrum that is building a decentralized alternative to centralized exchanges. Rather than simply building a spot Dex like Uniswap, the protocol envisions additional features such as margin trading, integrated borrowing/lending, trading from a mobile phone, simple signups and improved UX, single-sided LP deposits with no impermanent loss, fiat on/off-ramps, and an intuitive wallet for beginners and DeFi-natives alike.
Unstoppable Dex is meant to be a complete replacement for what a Dex can offer. It will provide the full infrastructure required to on/off-ramp users with fiat currencies and let them trade spot and with leverage and earn yield. This will make it possible for Unstoppable to give equal opportunities to access financial instruments to everybody regardless of their financial status.
The main user interface will focus on a clean, minimalistic UI covering the features needed for everyday trading, and at a later point, there will come an additional UI geared towards the power users and professional traders. This user interface will have support for professional trading features such as heatmaps, volume profiles, advanced order types, and API access for easy automation.


Unstoppable DEX provides 4 types of orders for spot trading, being:
Market orders
These are simple orders that execute immediately at the current market prices as long as the user has sufficient collateral.
Limit orders

These are orders to buy or sell a set amount of tokens at specific prices.
For example, a user can set a limit order to buy 1 $ETH at $1,800. When the price of $WETH reaches $1,800, the order will execute accordingly as long as there is sufficient collateral.
Limit orders are useful for users wishing to enter or exit at specific prices without having to monitor charts and execute them in real time.
Trailing Stop Orders

These are orders set to follow (trail) the current price by a chosen percentage, for a set amount of tokens. As the price rises, the stop price rises by the trailing amount, but if the price falls, the stop loss price doesn’t change, and the order is executed when the stop price is hit.
For example, a user can choose to sell 1 $WETH when the price of $WETH drops more than 20% from the current swap rate or its highest future price.
Trailing stop orders are useful for users that do not want to manually adjust a fixed stop loss, allowing it to trail after prices.
Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA)

These orders allow users to buy tokens over a period of time, at fixed intervals, regardless of its market price.
For example, say that a user wishes to purchase $1000 worth of $WETH. They can make a DCA order that purchases $100 of $WETH every 12 hours, 10 times.
DCA orders are useful for users wishing to accumulate tokens over a period without having to monitor prices, averaging the total cost.
Unlike other margin exchanges, the Unstoppable:DEX does not use perpetual contracts for its margin trading product, but a different approach that they believe is superior to trading derivatives.
Leveraged Spot
Spot leverage trading provides advantages such as avoiding the accumulation of excess debt in the system, supporting price discovery of the underlying asset, more sustainable price movements, and a lower likelihood for sudden price wicks that often lead to liquidations. Another important feature of fully backed spot trades is the sustainability and security for traders: all profits/losses are backed by the underlying asset, not synthetic. Because of this, the protocol itself can’t become insolvent or accrue bad debt that is owed to traders, who then end up missing out on their profits from open trades.
This model makes it possible for Unstoppable to tap into the deep liquidity of external Dexes like Camelot, Uniswap, GMX… instead of implementing a synthetic perp contract and a need for a funding rate to keep it in line with the underlying. This approach ensures that all trading positions are 100% backed by the underlying asset in a verifiable and transparent manner. As a result, traders only pay for borrowing funds in order to get leverage, and reactive rates will keep track of the utilization rate in order to adjust interest rates in real time on a block-by-block basis.
This is a solution where trades aren’t synthetic perps or futures contracts which act as a “receipt”. Instead, all trades are backed 1:1 with the underlying asset.
Traders still deposit collateral which they use to borrow funds to lever up, but instead of the exchange taking the other side of the trade, the borrowed funds are used to execute an actual spot swap. The swap is executed on the deepest and lowest-cost liquidity available.
As an example, if a trader deposits 100 $USDC and wants to achieve 10x leverage, they will need to borrow 900 $USDC. To do that, Unstoppable will use Uniswap to swap the 1,000 $USDC for $ETH. The remaining 900 $USDC come from liquidity providers.
This design means that the swap inherits the swap fees from the underlying liquidity source but in return, the trader gets:
Liquidations
When the leverage ratio of a trader’s position exceeds the maximum allowed leverage limit set by the protocol, the collateral owned by the trader can be sold off in a process called liquidation.
The purpose of this liquidation is to reduce the leverage ratio and bring it back within the acceptable limit.
For example, assume that 1 $ETH is trading at 1800 $USDC.
Fees
Fees at the start are as follows:
100% of fees are paid out to LPs and $UND stakers.
Fees are configurable by the multisig and will be adjusted as needed to create a healthy and sustainable ecosystem and a fair balance between LP yields and trading costs.
In Unstoppable’s Dex, it is possible for LPs to provide single-sided liquidity, enabling LPs to never be exposed to the other side of the trade. Consequently, LPs suffer no impermanent loss, since the rate is offset by Uniswap liquidity.
On top of that, the liquidity is split into tranches based on the desired level of risk exposure of any given user. Tranches are simply pieces of pooled liquidity split up by risk, to attract LPs with varying levels of exposure.
How it works
For example, when a trader wants to long $ETH, they borrow $USDC from LPs and buy $ETH. When a trader wants to short $ETH, they borrow $ETH from LPs and sell it for $USDC.
The only limitation on the size and quantity of positions that can be opened is the amount of liquidity provided by LPs for traders to borrow and increase their leverage.
Traders’ profits or losses are determined by the overall market movements and not influenced by the LPs. Since all trades are directly connected to the global DeFi market and every position is fully backed on a one-to-one basis, it implies that long and short positions operate independently and don’t require balancing for the system to function properly and securely.
Furthermore, this independence ensures that LPs are not exposed to traders’ profit or loss (PnL), and LPs will never be responsible for paying out traders’ profits.
Source of Real Yield
The Real Yield received by LPs is generated from the borrowing fees paid by traders when they borrow tokens from LPs to open leveraged positions.
The interest rate that LPs earn for lending their funds to traders increases as the utilization rate of the total deposited liquidity rises, indicating greater demand for borrowing from traders.
To ensure fair treatment for all participants, the borrowing interest rates are adjusted on a block-by-block basis to maintain a balance between supply and demand. This adjustment helps to optimize the allocation of funds and liquidity in the system.
For example, if a trader wants to long $ETH, they borrow $USDC from LPs to buy $ETH. To borrow this $ETH, the trader must pay a borrow fee which goes to the LP in the form of the borrowed asset. In this case, since $USDC was lent to the trader, $USDC is paid out to the LP.
Risks
The potential for LPs to incur losses arises in a specific situation where the liquidation system fails, resulting in inadequate and delayed liquidation of traders’ positions.
To address this risk, the team behind Unstoppable:DEX has prioritized minimizing such occurrences and ensuring the safety of LPs. The system has been designed with multiple layers of redundant monitoring and liquidation mechanisms. Additionally, the smart contract itself is programmed to automatically halt all trading activities if any instance of improper liquidation is detected, effectively preventing further risk accumulation in the system.
It’s important to note that while new trades and increased risk are paused during this time, users retain the ability to close their trades, withdraw funds, or adjust their LP positions as needed.
In the unlikely event of a liquidation failure, the system incorporates a safety module that assumes the first-loss risk and acts as a protective measure for LPs. This further safeguards the LPs and helps mitigate potential losses they may encounter.
Multiple layers of redundancy are in place to protect against the scenario that a trader’s position loses more money than the collateral deposited.
These layers are important to ensuring that LPs do not lose their deposits.
Layer 1 – Unstoppable Liquidation Engine
An off-chain liquidation engine monitors all positions and closes them automatically if the leverage of a position starts to exceed the maximum leverage allowed for the position’s market.
In most cases, this first line of defense will protect LPs but in the case that something does not work as intended and a position is not liquidated by our engine in a timely and orderly manner, the next line of defense is engaged.
Layer 2 – External Liquidation Engine
The liquidation opportunity is made available to third parties who are then able to liquidate the position for the protocol (and earn a profit for doing so).
Details on running an off-chain liquidation engine are to be released.
Layer 3 – MEV Searchers
The liquidation opportunity is exposed on-chain for MEV bots. (This is how liquidations on AAVE and Euler work for example).
These bots are constantly scanning for profitable opportunities, and the liquidation fee reward is one of them.
Layer 4 – The Safety Module
In the unlikely event that all of these layers fail to liquidate a trader’s position in a timely manner, the Safety Module kicks in.
The Safety Module’s function is to protect the LPs from loss of funds if a trader’s collateral is not liquidated quickly enough, resulting in a trader’s position losing more money than the collateral deposited.
If a liquidation were to be performed late putting the LP’s deposits at risk, then the Safety Module absorbs this loss, paying back the LPs.
Staking and Yields
Staking and Yields
Users may re-stake their LP position into the Safety Module in exchange for higher Real Yields.
When staking in the Safety Module, a user is betting that the liquidation engine and the multiple redundancy layers work as intended (and can of course run their own bot as an additional fallback). A user is also assuming the risk in case they are wrong.
In exchange, stakers earn a significant portion of Unstoppable fees in the form of Real Yield.

The goal of the Unstoppable Bridge is to make it seamless to move from fiat to crypto and vice-versa. Users will have access to easy-to-access on/off-ramps as a result of Unstoppable’s partnerships with fully trusted and regulated banks. This will make it possible to mint and redeem 1:1 backed stablecoins directly from a personal or corporate bank account. The ultimate goal is to become the “go-to” place on-chain that provides 24/7 1:1 backed FX swaps as well as FX leverage trading capabilities.
Note that the actual implementation of the Unstoppable Bridge is heavily dependent on the final agreements that can be reached by the protocol with banking partners.
Deep spot liquidity will make it possible to introduce RWA (Real World Assets) as well, such that users and protocol treasuries can keep earning yield on-chain while having their principal backed by off-chain assets.
Unstoppable plans to add FX pairs, where there will be one-to-one backed stablecoins for multiple currencies (euros, yen, dollars…). There will be an off-chain treasury holding the reserves at a regulated bank and storing the money in a variety of currencies. With the treasury in place, the protocol can mint the corresponding on-chain equivalent amount. This means that Unstoppable will be able to create a stablecoin for any currency that they have a banking partner for.
Unstoppable’s wallet aims to integrate advanced smart contract features with account abstraction in order to create a user experience that is intuitive and helpful to both beginners and advanced users.
The main goal behind this feature is to reduce the barrier of entry for new users and grow the existing market of DeFi users. Creating and managing a crypto wallet should offer a similar experience to creating a new account on a web2 service. In other words, if you can open an email/Facebook account you should be able to open a crypto wallet without any added complications.
Unstoppable’s wallet will be closely integrated with the Bridge for easy on/off-ramping. It will also be tightly coupled with the Dex to offer deep liquidity and drive volume with simple “one-click” abstractions. The goal is to abstract the complexities that come with providing liquidity or trading. Ultimately, even new, inexperienced, and non-tech-savvy users should be able to participate in crypto & DeFi. Think RobinHood for crypto but without compromising on the underlying values and self-custodial from the start. (i.e. no FTX/BlockFi etc possible).
Unstoppable is a protocol conceptualized as a DEX that is owned by its actual users. The project was built to offer a feature-complete alternative to centralized exchanges. This would be achieved by offering the following:
The expectation is that this will close the gap and current friction that most users face when interacting with dApps, crypto and DeFi. The ultimate goal is to make crypto usable in the real-world and accessible to everyone with a smartphone.
In the past (Q4 2022), Unstoppable has built a zero-fee $GLP auto-compounder that was released as a public good.
Unstoppable was also working on a product called TriGLP which would split the crypto and stablecoin elements of GMXs $GLP token and offer risk-adjusted real yield on the single-sided crypto and stablecoin parts. Implementation of this product was paused since multiple projects were working on GLP-based products which all would compete for the same GLP liquidity and the focus switched to developing the internal Unstoppable ecosystem – DEX, Bridge & Wallet.

However, the presence of a multitude of projects doing something similar (all of them competing for the same liquidity) as well as the fact that GMX is working on a V2 that supports synthetic assets trading (the GLP minting process will drastically change), made the team realize their own DEX, bridge, and wallet products should be prioritized. As a result, the Litepaper was published in January 2023.
Read the Litepaper
A living roadmap was introduced on January 3, 2024.
The project roadmap revolves around 3 core pillars:
One of the biggest hurdles for the mainstream adoption of Crypto and Web3 is the user experience (multiple networks, hexadecimal addresses, unintuitive interactions with smart contracts, seed phrases…). This is the most compelling reason for users to rely on centralized exchanges that will keep custody of their funds and give them access to a wide variety of services in a seamless manner. Centralized exchanges still dominate the industry despite big collapses such as Mt.Gox or FTX. This is due to their intuitive user experience, a wide range of services, simplicity to on/off-ramp, deep liquidity, integration with traditional finance, Web2 login, and no need to be responsible for keeping seed phrases safe…
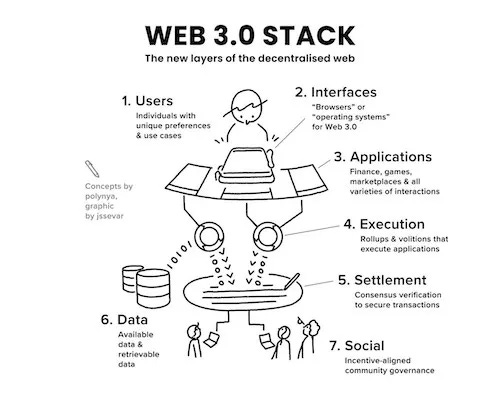
The value proposition of web3 infrastructure comes from giving users a high degree of self-sovereignty over their credentials, capital, and data. However, most of the time this comes at the expense of user experience, which is a significant detriment for mass adoption. As a matter of fact, one of the great challenges with making blockchain applications usable for average users is the security.
Due to the scope of the project, Unstoppable will be present across many verticals, ranging from decentralized exchanges (spot, derivatives, and forex) to bridges and wallets.
The spreadsheet attached below lets users modify the values in order to estimate the projected yearly revenue that can be achieved by Unstoppable.

View the Unstoppable – Addressable market spreadsheet here
By bringing FX pairs and RWAs (Real World Assets), Unstoppable is also anticipating times where RWAs will play a large role in decentralized trading. This exposes the protocol to a broader market share. For instance, protocol treasuries will have the option to keep their funds in assets that are fully backed by off-chain collateral.

The latest developments in Layer 2s, led by Optimism and Arbitrum, have made it possible for perpetual futures to be implemented on-chain. This was not possible in the past due to the high gas fees of the Ethereum network. Since the launch of GXM on Arbitrum, perpetual futures are one of the few products that have found product-market-fit (PMF) in the industry. This has led to the development of protocols like gTrade, Kwenta, Level…
The majority of decentralized exchanges offering leverage for trading rely on external oracle feeds and a liquidity pool where traders trade against LPs. This way, liquidity providers win when traders lose and vice-versa. However, this is not the way margin trade will work in Unstoppable. In fact, the mechanism design of Unstoppable’s margin trade makes it possible for both parties to obtain a positive outcome.

The core functionality for any margin exchange that offers leverage is to allow traders to borrow capital in order to increase the size of their positions relative to their collateral and then allow them to swap one asset for another. Most exchanges offer perpetual trading in the form of derivative contracts where, in the event that the odds of winning and losing are split 50/50, the liquidity providers will win, since they have an edge from collecting fees from traders. Once opened, the perpetual contract will keep track of the price of the underlying asset (usually informed by network keepers or off-chain bots that fetch prices from centralized exchanges) and the protocol will add a funding rate in order to maintain a neutral balance in the market between longs and shorts positions.
The funding rate is a system of periodic payments made to either short or long traders in the perpetual futures market. It is calculated based on the difference between the perpetual contract price and the spot price of the underlying crypto asset.
In a model where liquidity providers are forced to take the opposite side of traders, it is up to the protocol to enforce good risk management practices in order to ensure solvency. This often involves setting caps on open interest to control the overall exposure of the exchange to price movements and limit the potential losses of liquidity providers. For instance, protocols like GMX set limits on open interest in order to keep the protocol’s risk exposure in check. This is not needed in Unstoppable because the maximum available liquidity can only be capped by the available liquidity on the underlying Dex. Besides, if the utilization rates increase, so do the yield, and increasing yields attract more liquidity which makes bigger trades possible. This is often not the case in oracle-based perpetual exchanges, where traders might not be able to open large positions due to open interest caps enforced by the protocol.
The main difference with Unstoppable is that it does not use perpetual contracts. Instead, it offers leveraged spot positions. Traders deposit some collateral and can borrow funds to lever up. Next, instead of forcing LPs to be the counterparties to traders, Unstoppable builds on top of the deep liquidity provided by other Dexes. In this model, LPs are compensated with a borrowing fee that is paid by traders. At the same time, all positions are transparent and verifiable on-chain, meaning that anyone can observe how all trading positions are backed 100% by the underlying asset. This also helps when it comes to price discovery since all positions and swaps are actually executed on-chain and there is no need for balancing long/short positions.
So far, Unstoppable is taking an innovative approach that is unmatched by any other protocol and that aims to protect liquidity providers. As a matter of fact, there have been attempts in the past to produce losses for liquidity providers as a result of oracle manipulation attacks. This is achieved by manipulating the price of the underlying off-chain on a centralized exchange and then taking the opposite side of the trade on a perpetual Dex. These kinds of attacks would not be possible on Unstoppable because liquidity providers are not taking the opposite side of traders.
When it comes to interacting with web3, crypto wallets are the most important piece of a consumer’s journey. However, the UX of today’s wallets doesn’t fully reflect how critical it is to web3 usage and adoption.

Most users initiate their journey on centralized exchanges due to how simple it is to convert capital from fiat currencies to crypto assets. Despite the increase in the number of service providers offering on-ramping services (such as Ramp, Transak, or Moonpay), it is also worth noting that there are greater difficulties when it comes to off-ramping. This could be because wallet providers might want to get users onboard but don’t necessarily want them to leave.
Nonetheless, the vast majority of users do not end up transferring funds to Metamask or any other Web3 wallet because of all of the complexities associated with it (keeping custody of funds, and getting used to a user experience that is akin to Web2…). In addition to that, most wallets simply display a summary of a user’s holdings and have minimal functionalities.


Especially in countries that are more reliant on mobile phones – those without access to reliable internet connections, quick speeds, laptops, or computers – well-laid-out sites that are responsive were a big impulse for opening up access. For instance, the chart below shows the rate of internet adoption by country. A massive spike in growth can be observed with the onset of mobile and better UX with Web2.

With Unstoppable’s wallet and the integration of account abstraction, Unstoppable will be able to offer differentiating features that will make it stand out against its competitors such as a keyless and gasless experience, transaction batching, and social recovery.
When it comes to wallets, the most valuable features for web3 mass adoption boil down to:
The first deployment is on Arbitrum, but the protocol is open to exploring solutions on chains like Ethereum mainnet, layer 2 rollups, and even non-EVM compatible chains (although this will take additional development time).
In the live beta of the dex, users need to deposit funds in the protocol smart contracts to make trades, rather than letting people transfer money straight from their wallet for collateral. This process involves two steps: first, depositing assets into the smart contract (not into the wallet like a centralized exchange), and second, executing a trade. However, Unstoppable can and will offer both alternatives for making trades once the protocol is live.
After being audited, the smart contracts will be open-source, ensuring that only the user keys can move assets. The reasons to follow this approach are the proximity to offering a trading experience similar to a centralized exchange, and the ability for the protocol to offer advanced features like executing trades from a mobile phone using a different private key than the one that owns the assets. For instance, users will be able to deposit funds into their trading account and register a secondary key that’s allowed to execute trades but doesn’t have full custody over the assets.
The strength of the Unstoppable ecosystem lies in the synergies between its three pillars: dex, bridge, and wallet. This makes their products easily accessible to both institutional and retail investors, all while providing a seamless user experience that is akin to a centralized exchange.
Thanks to the development of core DeFi primitives, the ecosystem is able to offer infrastructure for a variety of services that can be built on top of the protocol smart contracts, such as structured products, savings and investment products, fiat-to-crypto rails…
After raising over 2,000 $ETH, Unstoppable’s runway will depend on a variety of factors, including the burn rate and the ratio of $ETH and USD expenses, which will show after the initial deployment phase has been finished. After Arbitrum, the protocol is considering several options for chain adoption, keeping an eye on Ethereum, ZK rollups, and other EVM chains. Deployment on non-EVM chains is also possible, but will take more development effort. It is also worth noting that a sustainability fund is part of the tokenomics, ensuring long-term revenue for platform development and improvements, and continued marketing. The sustainability fund will receive cash flow from staking and contribute to the platform’s continued development.
UND is the native token of the protocol and derives its utility from a dual token model that is set up to align the incentives of all participants in the ecosystem, from token holders to liquidity providers and traders.
The objective is to ensure a fair distribution while adequately rewarding all participants that contribute value to the ecosystem. This will also prevent predatory VCs, airdrop farmers, or mercenary capital from entering and remaining in the ecosystem for long periods of time.
$UND tokenomics reflect the belief in a fair and decentralized protocol that is owned by the community.

$UND is designed to be the backbone of the ecosystem. Only the public sale tokens and initial market liquidity will be distributed in unlocked $UND tokens, while the rest of the supply will start being distributed as $eUND (earned $UND), such as the team allocation, token incentives…
While $eUND tokens are fully transferable and can be transferred/sold OTC, $eUND can also be staked in the ecosystem like native $UND or be slowly vested over 12 months into unlocked $UND. This ensures that $eUND tokens cannot be sold on the open market at the expense of the community.
The utility and value accrual of the token is subject to changes over time in order to enhance the growth of the ecosystem and the value that is accrued to the token itself. As an example, there was a referral program before the token sale that rewarded users with a 5% kickback in real yield from all contributions made to the token sale through the user’s referral code.

Future use cases of the $UND token could include reduced fees across the Unstoppable ecosystem and use as collateral in a Masternode system.
The only way to earn $eUND is to earn it by providing value to the project and ecosystem. $eUND is a liquid token that is not locked or escrowed and can be freely transferred at any time. $eUND has the same properties as $UND and can be transformed into $UND at 1:1 by vesting it over 12 months linearly.
The game theory comes into play when it comes to strategies that take into account who is vesting and foregoing 12 months of real yield, who is selling OTC, who is staking… For instance, third parties could provide liquidity, Unstoppable might start a discounted buyback program, secondary markets for $eUND/$ETH or$ eUND/$UND could be created…
Staking $UND or $eUND may be staked in the platform and users may unstake at any time.
Staking currently allows token holders to lock their tokens in order to earn “real yield” from protocol fees.
In the future, stakers will get:

Unstoppable takes an approach of progressive decentralization. Over time, on-chain governance features will be implemented in order to progressively hand over control of the protocol to the DAO and the community.
In the beginning, the core team will be responsible for making decisions in order to move quickly and adapt to ever-changing market conditions. After that, the control of the DAO will be gradually transferred to the community. The vision is to have a community-owned project where there is no single point of failure from centralized control.
Main audits for the core products will be published right before the mainnet launch. There is also a Sherlock audit for Unstoppable’s Fair Funding product built on Alchemix, but this is not part of the core products.
Unstoppable code and smart contracts will be open-source and immutable, meaning that the code will provide full transparency and it will not be possible to alter the contracts’ logic as a result of an upgrade.
Unstoppable’s frontend code will be hosted on IPFS in order to ensure that no one can shut down the UI.
Since Unstoppable taps into the liquidity that is available on third-party Dexes, there is no need for the protocol to attract liquidity providers and expose them to additional risk. Instead, their risk exposure is only determined by liquidations. To protect against that risk, Unstoppable has a redundant monitoring infrastructure in place and everybody can additionally run their own liquidation engine/bot to help ensure the safety of the system.
The smart contract will pause all trading activity automatically whenever a bad liquidation is detected in the system (since this causes the protocol to accumulate bad debt). In this scenario, only the functionality for opening trades will be paused, in order to prevent any possibility to increase the risk in the system. Users will still be able to close their positions and withdraw their funds.
Two entities will be established: one off-chain and one on-chain. The reason for that is due to the complexities that come from having a DAO interact with traditional institutions, regulated banks…
The team is also supported by the work of freelancers and external contributors as needed, especially in the fields of smart contracts auditing, design and animations, UI development, and research.
There was no presale or private rounds available to Venture Capital or Angel investors.
The token sale took place on March 29 as a fair launch available to the community.

The protocol managed to raise 2,068 $ETH with more than 1,000 commits and more than 800 unique wallet addresses, at the final price of $0.195 per $UND.

