
Disclaimer: Please note that this project is no longer active due to a significant security incident that occurred on November 10th, 2023. This incident involved an exploit resulting in the unauthorized minting of approximately $6.7 million worth of unbacked R tokens, leading to the depegging of the R token. The aftermath of the incident has necessitated comprehensive recovery efforts, including the temporary pausing of all Raft smart contracts and the development of a detailed recovery plan. The finalized recovery plan resulted in a 42% recovery rate for affected users. This document remains available for historical reference and educational purposes only. We advise all readers to consider this context when reviewing the information presented below.
Raft is an immutable and decentralized lending protocol where users can take out USD-denominated loans against their $ETH derivative collaterals. In doing so, users will be able to borrow $R, a stablecoin that is hard-pegged to a price floor of 1 USD and that is overcollateralized. The protocol’s mechanism is designed to always retain a value of 1 USD for 1 unit of R.
In order to use Raft and borrow $R, the user must deposit collateral. Each Ethereum address is allowed to maintain only 1 open position.
Raft enhances the user experience by also allowing users to both deposit and withdraw the collateral token itself.
Interest Rate Vaults were introduced on September 14, 2023.
Users can generate $R through an interest rate vault by depositing a liquid staking token as collateral and paying a fixed interest rate in $R for the duration of the Position.
While all the vaults currently require 3000 $R as the minimum borrowed debt, they have different requirements for their minimum collateralization ratios, maximum leverage, annual interest rates, etc.
The vaults that are currently available are:
You can find more details here.
Loan repayments improve the collateral ratio of a user’s position and increase the amount of collateral available for withdrawal.
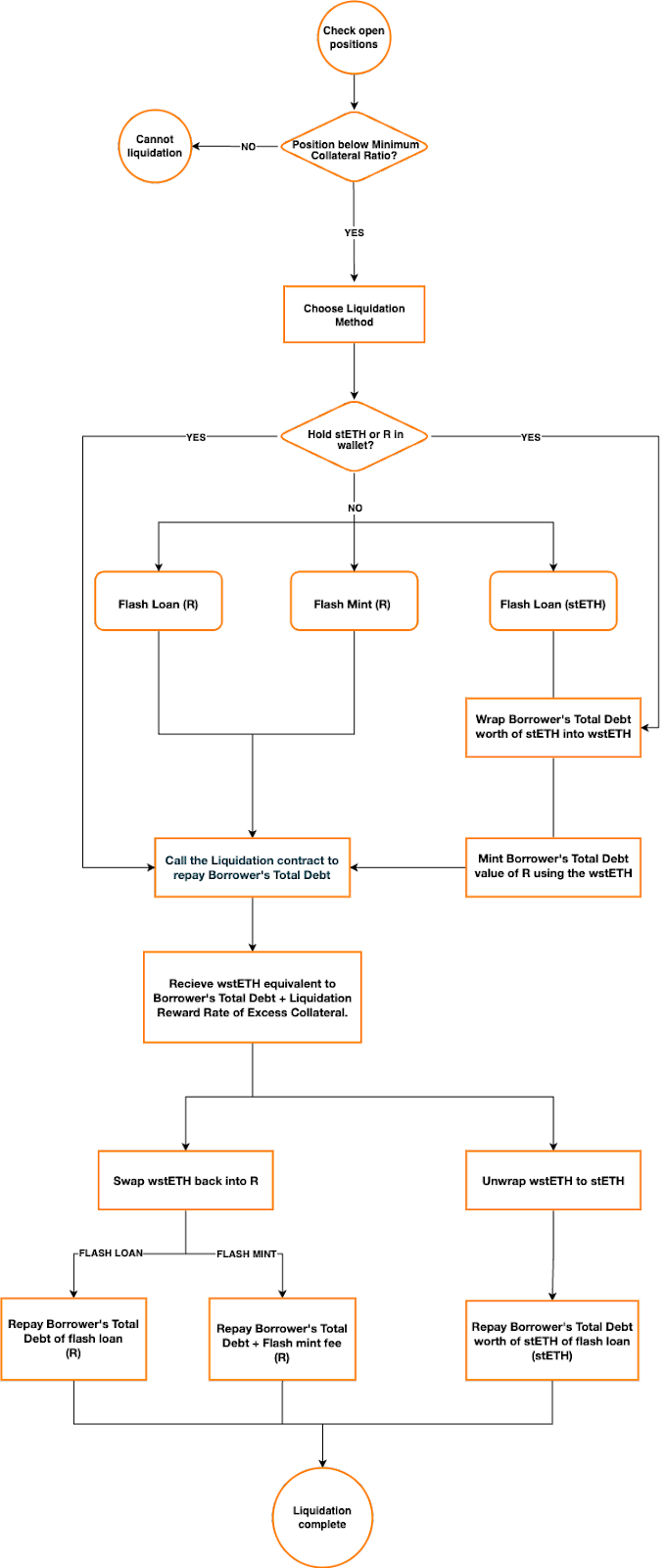
Liquidations ensure that each unit of $R is always backed by at least 1 USD worth of $wstETH. Liquidation payments are made by liquidators who pay off a borrower’s $R debt that is under the Minimum Collateralization Ratio. In return for this service, liquidators are compensated with a liquidation reward, and the insolvent borrower’s $wstETH collateral.
An account becomes eligible for liquidation when the position’s collateral falls below the Minimum Collateralization Ratio (i.e, 100% < Position’s collateral < 120%).
The liquidation process starts when the liquidator calls the smart contract responsible for performing the liquidation. When this happens, the liquidator proceeds to pay off the borrower’s total debt and, in return, receives the matching collateral and the liquidation reward.

In case the liquidator does not have enough $R in their wallet, they may use a flash loan or Raft’s Flash Mint module.
The liquidation reward and the protocol fee are in place in order to encourage users to support the protocol and help it remain overcollateralized. Similarly, this mechanism discourages borrowers from putting the protocol at risk by letting their positions be liquidated.
If the borrowers end up self-repaying or topping up their collateral, then they will not be charged any liquidation penalty.
LiquidationProtocolFee = ExcessCollateral – LiquidatorReward
The liquidation reward compensates liquidators for the risk they take on during the liquidation process. This is a dynamic percentage of the excess collateral based on the total debt, and its rates are set according to the table below:
| Total debt (R) | Liquidator reward rate |
| 3,000 R | 100% |
| 100,000 R | 100% |
| 1,000,000 R | 100% |
For values between the key total debt amounts listed, the liquidator reward rate is linearly interpolated between their corresponding liquidator reward rates:
The actual Liquidator Reward is simply the excess collateral multiplied by the above liquidator reward rate.
LiquidatorReward = ExcessCollateral * LiquidatorRewardRate
The liquidator reward rate was set to a flat 100% across the board on June 13, 2023.
Assuming a borrower has a debt position of 10,000 $R against 5 $wstETH collateral when $wstETH is trading at 2,180 $R.
The position is trading at 2,180 * 5 / 10,000 = 1.09 = 109% collateralization, which is below the 120% liquidation threshold.
A liquidator can step in and repay 10,000 R. In return, the liquidator will get the following $wstETH:
In total, the liquidator will get 4.587 + 0.4 = 4.987 $wstETH
In case the liquidator does not have enough $R tokens, they may use Flash Loan or Flash Mint.
A position below the minimum collateral ratio can be liquidated using the following procedures:
Raft offers a flash mint module that allows users to mint up to 10% of the total outstanding $R supply in one go with the condition that they will pay it back in the same transaction with a 0.01% flash mint rate. Users can use Raft’s smart contracts to operate directly without the need to rely on a separate money market or liquidity pool to flash R.
There is a 0.01% flash mint fee that is subject to change between 0% and 5%.
Flash mint transactions require lower gas fees than flash loans, which is particularly notable in low-liquidity conditions or when the costs from gas fees are high.
Flash mints play an important role during liquidations. Liquidators can flash mint $R tokens to repay a borrower’s debt and subsequently use the received collateral to swap back into $R and repay the flash mint, all within a single transaction.
Flash mint calculator: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1AzKbpQz1LTtdPNQ8CjhQJeM4DOQSVmGtDT8Tp_VYUg8/edit?usp=sharing
The flash mint module can also be used to obtain leverage on $wstETH.
In order to open a $wstETH leverage position through the flash mint module the following steps are taken.

In order to deleverage a $wstETH position in order to close all debts through a flash mint the following steps are taken.
Users can also use flash mints to adjust their positions to any other leverage level of their preference.
Redistributions ensure the stability and security of the platform by serving as the last line of defense in the unlikely scenario that liquidators fail to step in and liquidate all under-collateralized positions. During redistribution, the losses incurred by an undercollateralized position are fairly distributed among all positions in order to reduce the risk of systemic failure.
An account becomes eligible for redistribution when the position’s collateral falls below or equals 100% (i.e. position’s collateral <= 100%).
When a borrower’s collateralization ratio falls to 100% or below, a redistributor may trigger a redistribution, which entitles them to earn a redistributor reward. The remaining collateral and debt of the affected position will be proportionally split among other positions based on their collateral amounts, with higher collateral amounts receiving a larger share. Once the redistribution is complete, the under-collateralized position will be closed.
The redistributor is responsible for invoking the contract that will initiate the redistribution process. Due to the potential presence of high gas costs in the network, the protocol provides an incentive to the redistributor.
The redistributor reward rate is a dynamic percentage of the total collateral, where its rates are set according to the table below.
| Total collateral | Redistributor reward rate |
| 3,000 R | 3% |
| 100,000 R | 1.25% |
| 1,000,000 R | 0.5% |
For values between the key total collateral amounts listed, the redistributor reward rate is linearly interpolated between their corresponding redistributor reward rates.
The actual redistributor reward is the product of the total collateral and the redistributor reward rate.
RedistributorReward = TotalCollateral * RedistributorRewardRate
For instance, when the total collateral is 10,000:
![]()
Meaning that the liquidator will receive 2.87% of the total collateral, i.e. 287 R.
Assuming a position with 10,000 $R in debt and 5 $wstETH collateral when $wstETH is trading at 2,000 $R.
The position is trading at 2,000 * 5 / 10,000 = 1 = 100% collateralization, which indicates that the position is up for redistribution.
A redistributor will trigger a redistribution by calling the respective contract. In return, the redistributor will collect 0.1435 $wstETH (5 * 2.87%), equivalent to 287 $R.
The remaining 10,000 $R in debt and 4.86 (5 * 97.13%) $wstETH collateral are split 22% / 33% / 44% into positions B, C, and D respectively. 22% is calculated as 20 / ( 20 + 30 + 40). Hence, after the redistribution, the debt and collateral of all remaining positions will have increased, lowering their collateral ratio.
| Position | Debt | Collateral | Collateral ratio | Collateral weight | Debt change | Collateral change | New debt | New collateral | New collateral ratio |
| A | 10,000 | 4.86 | 97.2% | -100% | -10,000 | -4.86 | 0 | 0 | 0% |
| B | 30,000 | 20 | 133% | 22% | 2,222 | 1.08 | 32,222 | 21.08 | 131% |
| C | 40,000 | 30 | 150% | 33% | 3,333 | 1.62 | 43,333 | 31.62 | 146% |
| D | 50,000 | 40 | 160% | 44% | 4,444 | 2.16 | 54,444 | 42.16 | 155% |
All debt is quoted in $R and all collateral is quoted in $wstETH
In order to avoid single points of failures, Raft’s architecture accounts for two oracles: a primary oracle, and a secondary oracle. Both of these contracts can be upgraded by the team who are responsible for providing protocol contracts with the price of $stETH. If an anomaly in the reported price is detected, the system will fall back onto the secondary oracle or last good price as the source of truth. Abnormal conditions can occur under 3 scenarios:
Depending on the abnormal conditions that are detected, a fallback mechanism will be used:
Raft endorses decentralization not only through the use of immutable smart contracts, but also by relying on decentralized frontend user interfaces. Frontend Operators can construct separate frontend interfaces to allow users to interact with the underlying contracts, with the goal of improving the overall user experience. Alternatively, Frontend Operators can also integrate Raft into their personal applications, effectively introducing their user base to the Raft ecosystem and obtaining rewards for their efforts.
Frontend operators can apply for grants in order to receive economic compensation for their contributions to the Raft ecosystem.
This approach strengthens the censorship-resistance of the protocol and ensures that frontend interfaces are resilient to shutdown attempts by centralized parties. Additionally, Raft encourages all frontend operators to deploy their frontends on IPFS (InterPlanetary File System).
One-Step Leverage (OSL) was introduced on July 14, 2023.
OSL is a novel feature utilizing Flash Mint, allowing users to leverage up to 6x in a single step, boosting their potential earnings from liquid staking derivatives (LSDs). Users will be able to open, close or adjust their leverage accordingly.
The steps to generate LSD leverage through Flash Mint are the following:
The steps to generate deleverage LSD to close all debts through Flash Mint are as follows:
It is important to mention that the change in the R price in dollar terms could affect the amount of capital required to close the position. In particular, if the R price in dollar terms has increased since the Position was opened, more collateral will be required to repay the loan.
Adjust One-Step Leverage allows user to change the Position to any other leverage (within maximum limits) via Raft’s Flash Mint mechanism.
The steps to generate LSD leverage through Flash Mint are the following:
The $R Savings Rate was introduced on September 4, 2023.
It is an innovative program tailored to foster $R’s growth, stability, and utility as a predominant stablecoin, building upon the $Dai Savings Rate’s success.
Holders of $R can convert their $R tokens to $RR, which is a yield accruing ERC-20 token of the $R Savings Rate. While the quantity of the $RR token remains the same over time, this mechanism allows the token to grow in value according to the underlying APR, without having the user take action.
This can be done by:
Benefits of the $R Savings Rate includes:
$R follows the design principles implemented in CDPs such as $SAI (Single Collateral DAI) and $LUSD. However, Raft attempts to improve upon the original model by offering increased capital efficiency, flexible fees, more efficient and instant liquidations, and a more robust incentives system that strengthens the peg.
$R is the first USD stablecoin backed solely by $stETH, which is a capital-efficient and censorship-resistant collateral asset by which Raft will attempt to prevent failures of the past such as the USDC depeg. As a matter of fact, the USDC depeg was caused by its dependence on collateral held by banks. Similarly, DAI suffered the same fate because more than half of its collateral is made of USDC.
R is designed from first principles to belong to a category of non-fiat backed stablecoins and which are fully backed by uncensorable and decentralized crypto assets like $stETH. This way, each unit can be instantly redeemable without the intervention of any intermediary or third-party.
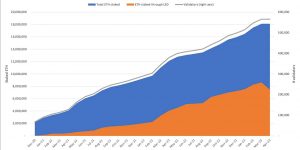
The timing of the protocol launch was heavily influenced by the proximity to Ethereum’s Shanghai/Capella upgrade on April 12. At the time, there was a total of 17.8M $ETH (~$32B) deposited on Ethereum’s PoS chain which could not be withdrawn (~15% of the circulating supply). The success of the upgrade enabled withdrawals and any uplifted any prior liquidity constraints that had been present in the past.
Raft’s core team estimates an increase in the number of users who will stake their $ETH, earning an average yield between 4-6%.
Lido staking APR: https://dune.com/queries/570874/1464690
At the time of the Shanghai upgrade, even though only 15% of the total $ETH circulating supply was staked in the PoS network, close to 95% of the staked $ETH on Liquid Staking Derivatives was dominated by 3 players: Lido, Coinbase, and Rocket Pool.
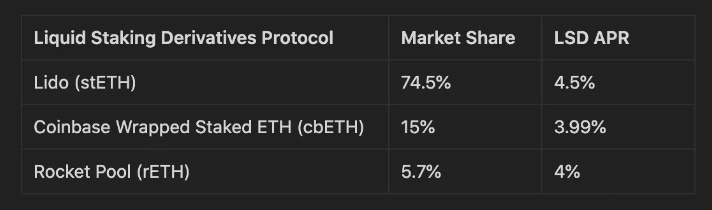
Some of the reasons that led to the dominance of Lido include:
There is no official roadmap published yet, but some of the soft targets includes:
Raft is built by Tempus, a venture DAO backed by investors such as GSR, Lemniscap, Wintermute, and Jump among others.
The team includes:
Since the release of Single-Collateral DAI in 2017, the adoption of decentralized stablecoins has increased significantly. $R is an attempt to improve the design principles behind consolidated CDP models such as SAI (Single Collateral DAI) and LUSD. Most CDP-based borrowing frameworks (this is not the case for Liquity) apply variable borrowing rates in order to encourage or discourage borrowing. With this model, borrowers don’t grapple with the cost right away. In actuality, the interest paid by borrowers is not the net outcome of their own debt, but of the debt incurred by other borrowers. Because of this and the need for governance, Raft has opted out of this model and has chosen to build a decentralized and direct feedback system built on one-off fees.
Nowadays, centralized and fiat-backed stablecoins still remain the most dominant in terms of adoption. However, users need to trust a centralized issuer to have a banking infrastructure that is capable of backing every unit of stablecoin. This centralization creates a single point of failure and can make the stablecoin vulnerable to issues such as regulatory crackdowns or bank failures. Similarly, stablecoins like USDC and USDT suffer from lack of transparency, counterparty risk and limited accessibility.

Recent events such as DAI’s depegging from USDC have highlighted the need for a more decentralized stablecoin that relies less on centralized entities and carries less regulatory risk. Therefore, Raft falls back on Lido’s $stETH as the most capital-efficient and decentralized asset to back the $R stablecoin.
The stablecoin trilemma is a concept that refers to the difficulty in achieving three key properties of a stablecoin simultaneously: stability, decentralization, and scalability.
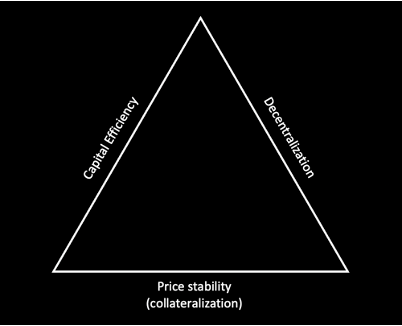
Raft attempts to solve for the trilemma with the issuance of $R, a stablecoin that is backed by a yield-bearing collateral asset, $stETH, and whose minting relies on immutable smart contracts whose logic is transparent and can be audited by anyone. While its governance-minimized approach makes it highly decentralized and the use of $stETH instead of $ETH is a big improvement in terms of capital efficiency, $R still requires excess collateral in order to be minted.
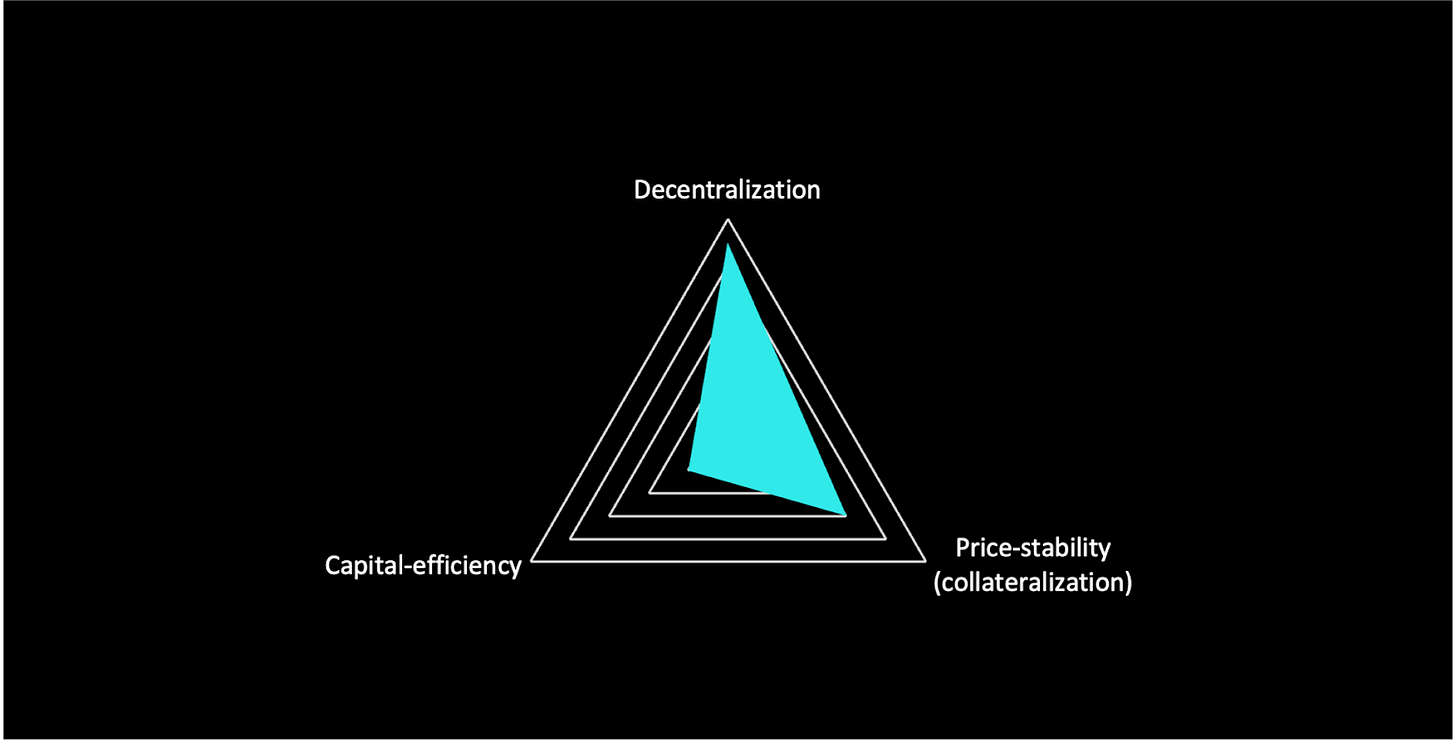
Every unit of $R in circulation is backed by excess collateral, meaning the value of the collateral is higher than the value of debt being taken. Thanks to the combination of a hard and a soft peg mechanism, $R can be used as a unit of account across DeFi, meeting similar functions to money.
In DeFi, a large percentage of the $stETH circulating supply is often deposited in protocols like Aave (v2 and v3) or Maker (Vault A and Vault B) in order to leverage up on $stETH collateral. However, these platforms have the problem that users are forced to manually repeat the borrowing and re-depositing cycle multiple times (looping) in order to achieve a significantly leveraged position. This is not only time-consuming, but also very inefficient in terms of gas costs, and high borrowing fees which leads to a poor user experience and introduces complicated math that opaques the user’s liquidation threshold.
To solve this problem, Raft introduces a “one-step leverage” feature that makes leveraging $stETH a much more seamless and gas-efficient user experience. This is achieved with Raft’s flash mint module.
This process takes place in Raft with just one click. The user just needs to select the amount of leverage and slippage and click “Execute”.
The benefits of this process stand out from its simplicity and capital efficiency, allowing users to get access to leverage cheaply and with just one click.
The following table summarizes how Raft compares to other CDP models where users can borrow a stablecoin such as Liquity and MakerDAO:
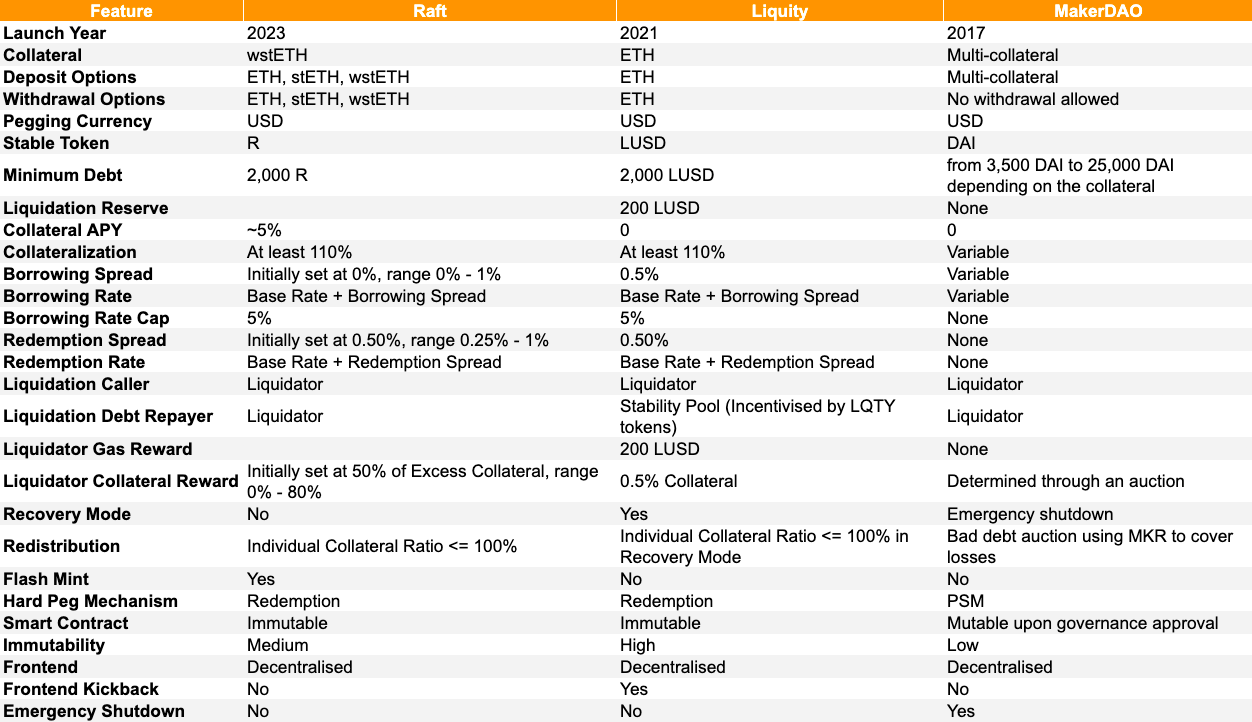
It is worth noting that, unlike Liquity, Raft will not follow a dual token model at launch. For instance, Liquity utilizes two incentive mechanisms in order to remain solvent and stabilize the $LUSD peg:
Raft is also different from other CDP-based protocols because it only accepts one asset as collateral: $stETH.
Some protocols that are similar to Raft are MakerDAO, Liquity, Abracadabra, Angle, QiDAO, Reflexer …
Raft’s one-click leverage feature also allows users to get up to 11x leverage on their $stETH holdings (at the expense of a flash mint fee). While this level of leverage is also possible with Liquity, it still outperforms what users can get in other money markets or lending protocols when folding their positions. This is because users benefit from the increase in price of $stETH they hold as a result of leveraging on Raft along with the additional staking rewards they receive which do not exist on Liquity or are reduced due to the lower leverage and high annual fees on other money markets like Aave and Maker.

Raft is available on the following chains:
Instead of selling their $stETH, users can use Raft to have access to liquid funds.
Similarly, users can uso the one-step leverage feature to access leverage on $stETH in a single atomic transaction:
Raft’s primary user base consists of $stETH token holders who want to borrow a stablecoin against their $stETH in a capital-efficient manner. Instead of selling their $stETH, they can use Raft to have access to liquid funds.
With Raft’s one-click leverage feature, users can get up to 11x leverage on their $stETH holdings at no cost.
(Minimum Collateral Ratio) / (Minimum Collateral Ratio – 100%) = 6
(120%) / (120%– 100%) = 6
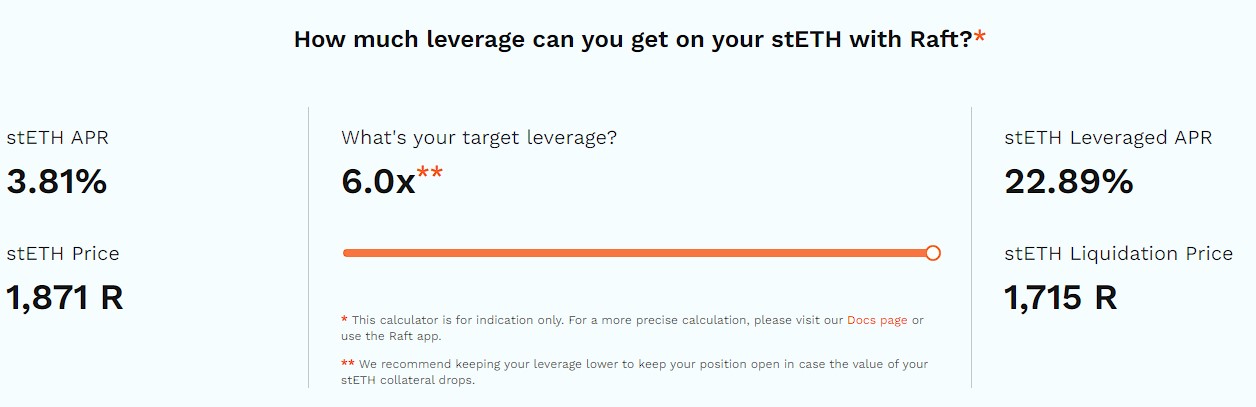
Raft provides users with a capital efficient and decentralized way to take out loans against $stETH. There is a requisite of a minimum 120% collateral ratio that allows users to borrow in a USD-denominated stablecoin, $R, at a 0% interest rate and no minting fee. As a result, borrowers do not have to worry about constantly accruing debt. Besides, the core components of the Raft contracts are immutable and have no admin keys.
R is USD-denominated stablecoin backed by $stETH (Lido Staked Ether) with a combination of a hard peg and a soft peg.
The Peg Stability Module (PSM) was introduced on September 4, 2023.
The PSM is a smart contract that allows users to swap between two assets at a fixed exchange rate and its core function is to stabilize the price of $R via a hard peg mechanism, fixing it at $1, which is done via swaps between $R and $DAI at a fixed rate, enabling a tight and stable peg.
The PSM enables users to perform the following actions:
The utility of the PSM is evident during periods in which the $R price deviates from $ 1:
In cases where the $DAI price in US dollars drops below a specific threshold, the PSM will stop functioning automatically. This is a crucial safety feature designed to safeguard the stability of the $R token and its peg to $DAI. It adds an extra layer of risk management, ensuring that the system can respond to severe market fluctuations effectively.
The PSM is an essential element of the overarching Raft economics because it allows the protocol to accumulate an external asset, $CHAI, whose yield accrues to $R Savings Rate depositors. The relationship between the PSM and the $R Savings Module can be depicted as follows:
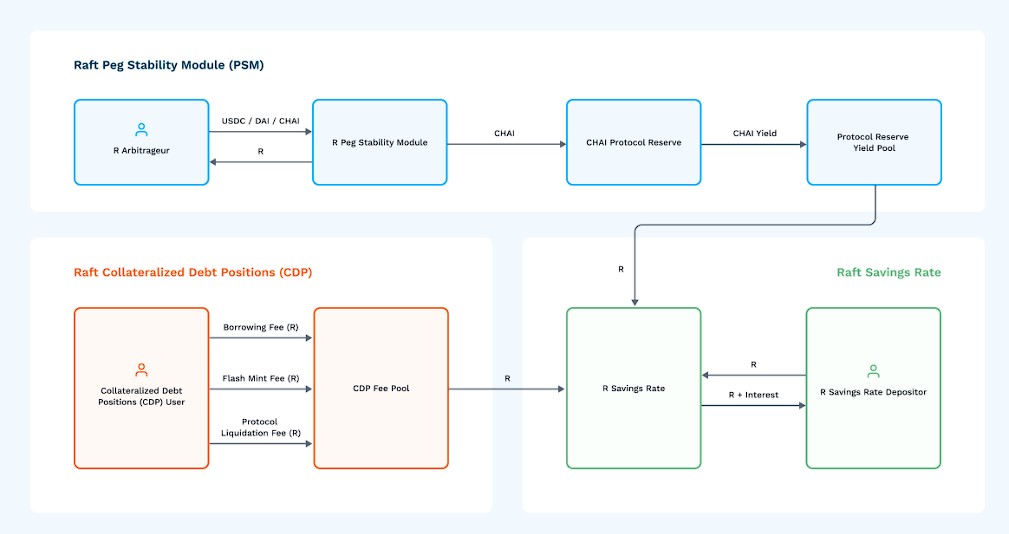
Raft seeks to improve liquidity conditions for the $R stablecoin by providing liquidity across numerous market pairs in a series of AMMs and centralized exchanges. Besides, in order to encourage users to contribute to R’s liquidity, they can deposit $R into liquidity pools alongside other assets and receive incentives in return.
The tokenomics for $RAFT was introduced on September 26, 2023.
The token is designed to promote active involvement from the community, improve liquidity provision, and empower token holders to have a say in the governance of the protocol. Generally, the token provides 2 functions to holders, staking, and governance.
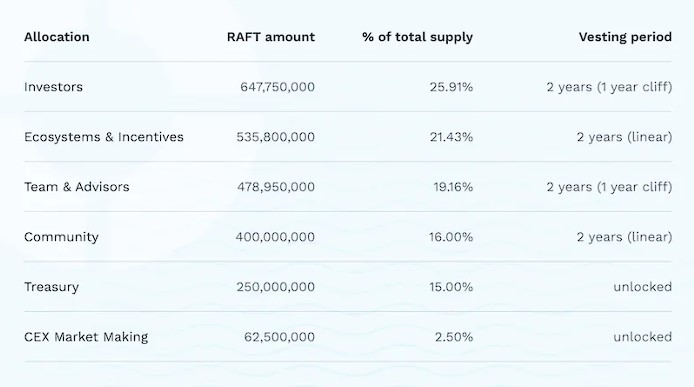
The allocation of $RAFT is as follows:
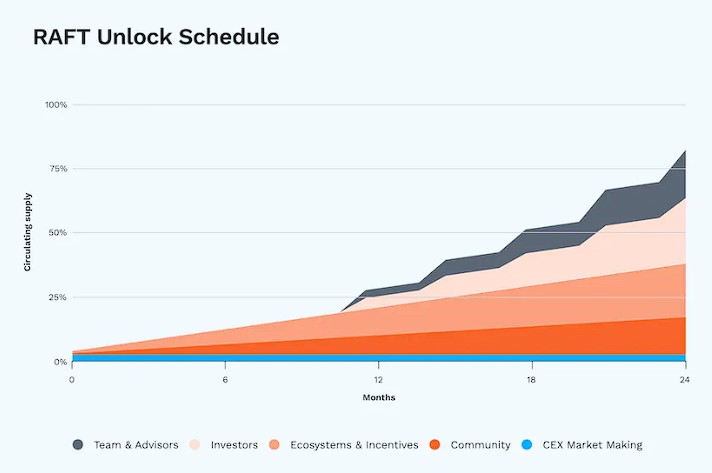
The unlock schedule is as follows
The veRAFT mechanic is inspired by Balancer’s 80:20 system and offers significant benefits. It allows liquidity providers to benefit from RAFT’s potential growth while reducing the risk of impermanent loss, providing a balanced approach to participation and security.
Holders of $RAFT tokens can choose to stake $RAFT into a liquidity pool on Balancer, consisting of 80:20 $RAFT:$R tokens. They will then receive BPT tokens representing their veRAFT position.
They can then stake the BPT tokens into the Raft staking contract and lock their staked positions for up to 2 years, where 10% of the total $RAFT tokens will be distributed over 3 years.
Holders of veRAFT can then vote on key protocol decisions to drive the growth of Raft while earning $RAFT token rewards.
The design is aimed at encouraging both immediate participation and long-term commitment. The duration for which tokens are staked directly impacts both voting power in governance decisions and the portion of $RAFT token rewards received. Longer staking periods lead to a larger share of rewards for the stakers.
In the future, the Raft DAO may explore the option of distributing protocol revenue to veRAFT holders as the Raft protocol progresses toward sustainability.
Wave 1 of the $RAFT airdrop was announced on October 11, 2023.
Wave 1 of the RAFT airdrop is intended to reward the users who contributed to Raft’s growth and success during the early phase of the project. This includes users on both Ethereum Mainnet and Base. A total of 604 wallet addresses qualified for the Raft Wave 1 Airdrop.
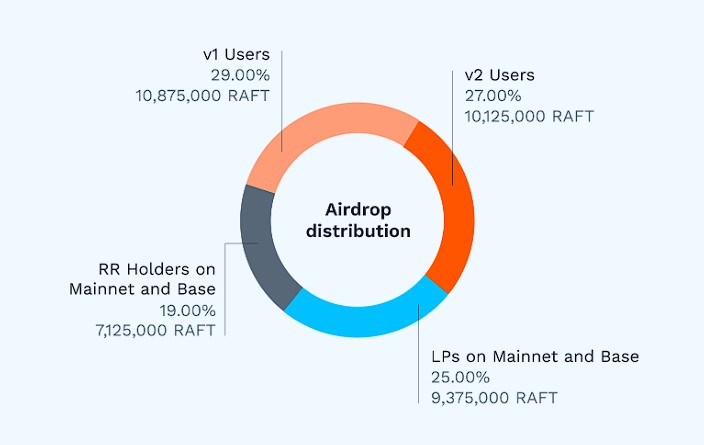
It consisted of 4 main criteria, utilizing a point system for token allocation. Users could be eligible for multiple criteria, providing additional points.
The snapshot was taken on September 28, 2023 at mainnet block 18235432, with 37,500,000 $RAFT being allocated, representing 1.5% of the total $RAFT supply.
The following table provides an overview of the qualifying actions that were accounted for Wave 1.
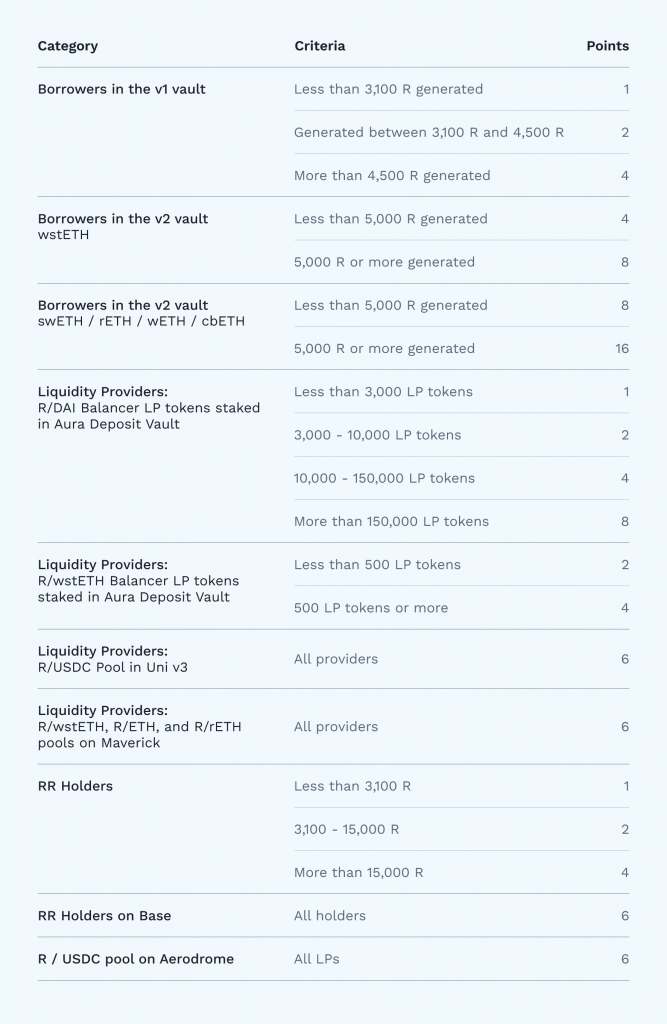
The following graph indicates the allocation of $RAFT.
The Raft protocol is immutable and its core smart contracts cannot be upgraded. As a result, there is no centralized point of control over the protocol’s core mechanism. Besides, there is no way to pause the smart contracts. Consequently, Raft follows a governance-minimized approach in order to remain agile and user-focused while maintaining robust security.
Raft’s governance-minimized approach offers the following advantages:
At the beginning, governance decisions will be enacted with a ⅗ multisig controlled by a combination of Raft and outside members. Moving forward, Raft will follow a progressive road towards decentralization. Nonetheless, the scope of governance is intentionally limited to 3 main areas.
In the article for the tokenomics of $RAFT, introduced on September 26, 2023, holders of veRAFT would be able to vote on key protocol decision to drive the growth of Raft while earning $RAFT tokens.
These include:
The liquidity committee is responsible for managing and deploying incentives across different pools. By having a dedicated committee, the protocol can ensure that it can adapt to the ever-changing conditions of the markets and optimally allocate incentives that will foster liquidity and improve $R’s peg stability.
The actions of the liquidity committee do directly affect the hard peg mechanism of R. Instead, the focus is on providing ample liquidity to support the soft peg to $1, with the objective to allow users to confidently trade $R with minimal slippage or price impact.
The primary role of the committee is to assume the following responsibilities:
Initially, the liquidity committee consists of 3 members from Raft’s core team, which will form a multisig in order to allow for secure and collaborative decision-making. Over time, as the governance structure becomes more community-driven, the liquidity committee will seek to decentralize its operations.
The governance forum was created and announced in an article posted on June 12, 2023. It is part of the fully decentralized process that Raft aims to achieve.
The forum will serve as a space for Raft’s community to discuss proposals, voice their opinions, and actively participate in decision-making to shape Raft’s future.
There are major technical challenges associated with stablecoins. Regardless of the decentralized nature and censorship resistance of collateral assets, Raft’s core smart contracts are immutable, and the core logic cannot be changed after deployments. What’s more, the protocol relies on a governance-minimized approach to ensure that contract updates are safe and smooth, particularly for critical stablecoin parameters.
Raft’s codebase was not forked from another protocol and has been built from scratch. Since the protocol operates as a fully automated and algorithmic decentralized system, collateral assets are transferred from users to the protocol without the intervention of any person or legal entity. Because of that, users who interact with the protocol are subject to the rules set forth in Raft’s immutable smart contracts.
Raft has been audited by Trail of Bits and Hats Finance.
A bug bounty program was launched on Hats Finance on June 7 2023.
Raft is exposed to oracle risk due to requisite for precise pricing and the liquidation logic implemented by its smart contracts. Oracle price feeds are used for assigning a value to outstanding loans and estimating which ones are in default. The manipulation of oracle price feeds can force the protocol to liquidate loans that are not in default, thus causing a loss of customer funds.
The key parts of the protocol are immutable and their code logic cannot be upgraded or modified by any centralized entity. Nonetheless, the deployer still has admin rights to turn on protocol fees (which are initially hardcoded to certain parameters) if governance chooses to do so at a future date. These parameters will be initially set and monitored by the liquidity council,
Events like the depegging event experienced by $DAI and $USDC in March 2023 showcase the importance of diversifying $R’s liquidity sources as well as minimizing counterparty risk and single point of failures. By design, R only has exposure to stETH. Additionally, the liquidy committee takes into consideration the possibility of anchoring $R to decentralized assets like $ETH. This way, they can create a more resilient and diverse liquidity pool that provides more stability and reliability for its token holders.
Additionally, developers also face the challenge of having to manage the high gas costs of the Ethereum network. Raft also has exposure to market risk associated with the safety of liquidations, market volatility and cascading liquidations. Borrowers need the protocol to remain solvent, otherwise they will not be able to get their $ETH collateral back.
On 10 November 2023 at 18:59:23 UTC, Raft encountered a complex security incident, resulting in the minting of ~$6.7 million unbacked $R, subsequently, the attacker sold $R, causing $R’s depeg.
The sequence of actions taken by the attacker was as follows:
The primary root cause was a precision calculation issue when minting share tokens, which enabled the exploiter to obtain extra share tokens. The attacker leveraged the amplified index value to increase the worth of their shares, allowing them to redeem a nominal amount of rcbETH-c for a significant quantity of cbETH and subsequently borrow substantial amounts of R.
A police report was filed, and a recovery plan was finalized on November 23, 2023.
As a result, a 42% recovery rate was effected in the form of $DAI, distributed to affected users.
Investors includes the following: